Benefits and Risks of At-Home Thyroid Tests
According to the American Thyroid Association, about 20 million Americans have some type of thyroid disease.
Approximately 60% of people with thyroid disease are unaware of their condition[i]. Hormones produced by the butterfly-shaped gland participate in a number of functions in the body.
Thyroid diseases can affect our quality of life and increase the risk or worsen other health conditions. Keeping hormones in a normal range is vital for good health. People with thyroid disease need to pay close attention to the hormone levels.
Testing can be of huge help, and nowadays, you have the option to use at-home tests.
How do they work?
What are the benefits and potential risks of at-home tests?
Should you try them?
What are the at-home tests?
Regular tests are important for the management of many health conditions. Traditional testing is performed in clinics and hospitals, but nowadays, due to a hectic and busy lifestyle, it may not be practical for many people to get tested this way.
It is needless to mention insurance plans, costs, and other factors. With the rise of technology and science, we have easy access to at-home tests, which are cost-effective, quick, and confidential, according to the FDA[ii].
Home tests can help detect possible health conditions even when no symptoms are present, thus allowing a person to get early treatment and decrease the risk of complications.
Additionally, at-home tests can also help users monitor their health condition, which is crucial for successful management or treatment of that disease.
How do home thyroid tests work?
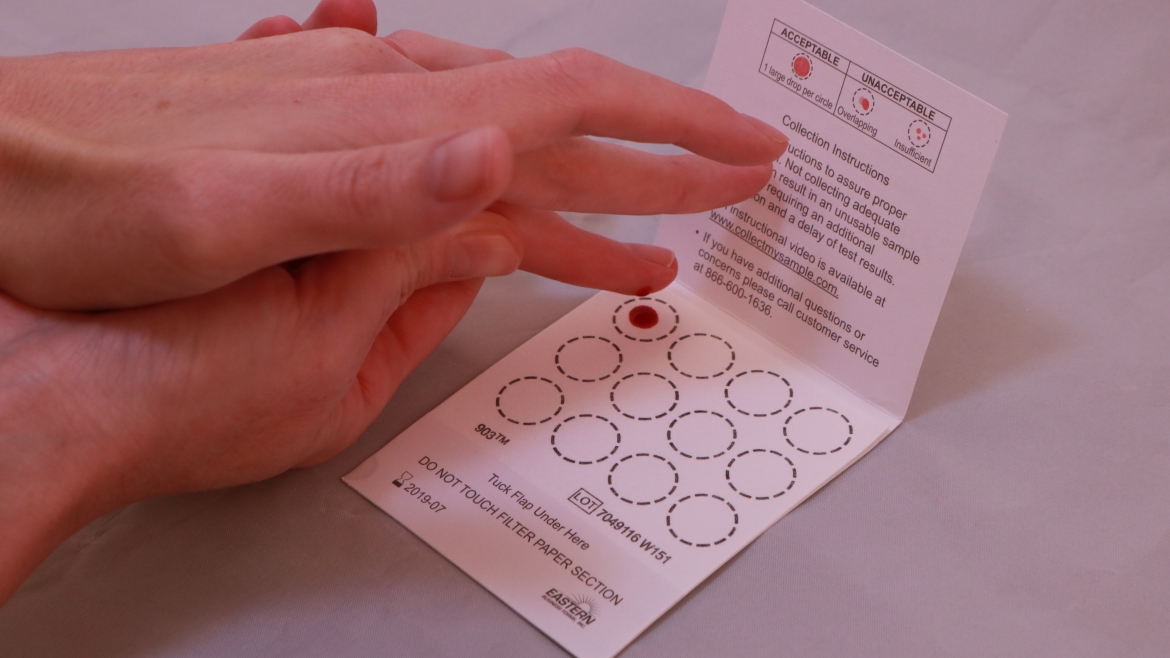
Nowadays, people can buy and use at-home tests for a wide spectrum of health conditions ranging from sexually transmitted infections to thyroid diseases. If you haven't used a home thyroid test before, you are probably wondering what that is and how it works. The at-home thyroid tests are kits that allow users to measure thyroid hormone levels in their homes.
The whole process is straightforward and easy. You can buy these tests online or in pharmacy. While every manufacturer may have a different system, a user is usually required to enter a barcode included on the kit on the official brand website. Use the kit to collect a blood sample (a single prick is enough) and return the kit. Then, the board-certified physician reviews the results which are available only to the patient on the platform.
Not only do they come at relatively affordable prices, but now, during the holiday season, there are discount codes on the manufacturer websites which allow users to get their kit for less.
What at-home thyroid tests check?
We can divide at-home thyroid tests into two categories: those that check thyroid hormones and tests for antibodies. Below, we are going to elaborate on them further.
Home thyroid tests for hormones usually check:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates the thyroid gland. The normal range of TSH depends on the age of a person and whether they’re pregnant or not. It is usually considered that TSH levels in the range of 0.4 to 4.0 mU/l (milliunits per liter) are normal. However, it is also worth mentioning that the normal range may vary from one laboratory to another. High levels of TSH indicate a person might have hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid, a common condition where the butterfly-shaped gland produces an insufficient amount of hormones. On the other hand, low TSH levels may occur due to hyperthyroidism, too much iodine in the blood, too much thyroid hormone medication, Graves’ disease (an autoimmune condition that causes hyperthyroidism), and presence of excessive levels of a supplement containing thyroid hormone[iii]
- T3 – triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. A vast majority of this hormone in the body binds to the protein, but some of it doesn't bind, and it is referred to as free T3 (fT3). Free T3 circulates unbound in the blood. Levels of this hormone can help determine whether a person has hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Some tests check total T3 while others free T3. According to the American Thyroid Association measurement of free T3 is often not reliable and typically not helpful for healthcare providers[iv]. While the normal range may differ from one laboratory to another, in most cases, normal results of T3 measurement fall between 100 and 200 ng/dl (nanograms per deciliter). Low levels of T3 indicate the presence of hypothyroidism, while high levels could mean a person is hyperthyroid. Other factors may also alter the balance of this hormone, such as starvation. It is worth mentioning that abnormal levels of T3 alone don't necessarily mean a person has thyroid disease. That's why it's useful to measure other hormones (T4 and TSH) too and see the doctor who will diagnose the problem
- T4 – also known as thyroxine, this hormone is produced by the thyroid gland. Just like T3, some portion of this hormone is not bound to proteins and exists in free form (free T4 or fT4). Tests can measure free T4 or total T4, which checks both bound and free hormone levels. Additionally, tests that measure T4 more accurately reflect how the thyroid gland is functioning when checked with TSH. For example, elevated TSH and low fT4 indicate the presence of hypothyroidism, while low TSH and high fT4 point to hyperthyroidism. Generally accepted normal values of total T4 in adults range from 5.0 to 12.0 µg/dl (micrograms per deciliter), while normal results of fT4 are between 0.8 to 1.8 ng/dl
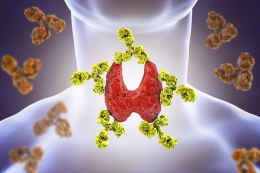
Besides tests that check thyroid hormones, it is also possible to get the kits that check thyroid antibodies. More precisely, they usually check TPO (thyroid peroxidase antibodies). Thyroid peroxidase antibodies are a marker for the presence of autoimmune thyroid disease. Test results positive for TPO antibodies are found in 95% of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition, and the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
About 50% to 80% of Graves’ disease also test positive to TPO antibodies. Moreover, people who test positive to TPO antibodies have a higher risk of further thyroid dysfunction[v].
Advantages of at-home tests
As seen throughout the post above, at-home tests for thyroid hormones have a number of benefits. We are going to sum them up below:
- Highlighting the problem – millions of people have a thyroid condition, but they are not aware of it. At the same time, many men and women are in the high-risk group of developing some thyroid disease, but they are not quite sure whether they have it or not. At-home tests highlight the potential problem. Results indicate whether there are imbalances in hormone levels which would point to the existence of a thyroid condition. That way, a person gets a much-needed boost to see the doctor who will diagnose the problem. When it comes to thyroid diseases, effective management requires prompt treatment and diagnosis, and at-home tests can be the nudge in the right direction
- Easier management of thyroid disease – fluctuation of thyroid hormones induces a wide range of symptoms that vary in intensity from mild to severe. People with thyroid disease receive treatment to normalize hormone levels, and at-home tests can make this process easier. Test outcomes can also give doctors an in-depth insight that would help them modify the treatment when necessary
- Cost-effective – one of the most important benefits of at-home tests for thyroid is their cost-effectiveness. They come at reasonable prices and make it possible for a larger group of people to test their hormone levels and modify their lifestyle to keep them in a normal range
- Practicality – home tests are a practical solution today when most people have a busy lifestyle. They can be ordered online and done in the comfort of your home, without having to drive around, sit in a waiting room, and other things that are so common with “traditional” testing
- Accuracy – at-home thyroid tests are accurate and precise, which gives users more confidence. This also leads to proactive management of thyroid disease, or they get the motivation they need to see the doctor if they refused to do so prior to taking an at-home test
Disadvantages of at-home tests
At-home tests have a lot of benefits, but they also have some disadvantages or limitations. However, these disadvantages refer to cases when people rely on at-home tests only. For example, a person may buy a home thyroid test and completely ignore routine checkups at the doctor’s office[vi]. This happens because the results give people a false sense of security, thinking there is no need to see their doctor.
Generally speaking, at-home tests are not invasive and do not induce some side effects. But, if you are not sure about how to use them, consult your doctor or pharmacist who will instruct you about the whole process.
Do you need to check thyroid hormones?
At-home thyroid tests can be incredibly useful, but it’s impossible not to ask whether you really need them. Most people are reluctant to take any kind of test because they don’t want to face potentially negative results. But in order to diagnose the problem in its early stages or to improve the management of some thyroid disease, it is crucial to check thyroid hormone levels regularly. This is particularly important for women who are more likely to develop some thyroid disease than men.
Besides existing thyroid disease, you also need to check thyroid hormones if you are in a high-risk group of developing some condition that affects the butterfly-shaped gland. These risk factors include:
- Being a woman
- Being older than 50 (the aging process increases the risk of thyroid problems)
- Family history of thyroid diseases
- Exposure of the neck to radiation
- Taking certain medications such as amiodarone, lithium, and others
- Being a smoker
- Low intake of iodine
Important to remember
Even though at-home tests offer significant benefits to users, they do not replace periodic visits to the doctor. This is particularly the case with people who have some thyroid condition. At-home tests allow for easy monitoring of thyroid hormone levels, but they are not intended to replace doctor visits and treatments recommended for a condition affecting the butterfly-shaped gland.
Consult the doctor about at-home tests and ask whether they recommend some specific kind. When worried about test results, you should express the concerns to your doctor. At-home tests, when used adequately, can be an asset to the management of thyroid disease, but bear in mind they don’t downplay the significance of doctor visits and treatment.
Tips to protect the thyroid gland
At-home tests may be the motivation you need to become more proactive about thyroid health. Make sure to adjust your lifestyle in order to support the function of this gland. The following tips can help you:
- Maintain weight in a healthy range
- Make sure you are taking enough iodine (this is usually not a problem for people in developed countries)
- Cook brassicas because when consumed raw they can be damaging for thyroid
- Consume more nuts
- Avoid starving yourself or adhering to fad diets
- Manage stress
- Quit smoking
- Eat a well-balanced diet
- Get enough sleep
- Avoid BPA
- Exercise regularly
Conclusion
At-home tests are a fast, convenient, and precise method of getting more insight into thyroid hormone levels. They are easy to buy and use.
However, they do not replace routine checkups at the doctor's office and treatment recommended by your healthcare provider.
References
[i] General information/Pressroom, American Thyroid Association. Retrieved from: https://www.thyroid.org/media-main/press-room/
[ii] Home use tests, FDA. Retrieved from: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/vitro-diagnostics/home-use-tests
[iii] What is a TSH test? WebMD. Retrieved from: https://www.webmd.com/women/what-is-tsh-test#1
[iv] Thyroid function tests. American Thyroid Association. Retrieved from: https://www.thyroid.org/thyroid-function-tests/
[v] Sadler C. (2012). Thyroid peroxidase antibodies. Clinician Reviews, 22(4):19. Retrieved from: https://www.mdedge.com/clinicianreviews/article/72387/endocrinology/thyroid-peroxidase-antibodies
[vi] Terrie YC (2013). At-home test and monitor kits. Pharmacy Times. Retrieved from: https://www.pharmacytimes.com/publications/issue/2013/september2013/at-home-test-and-monitor-kits



















































Leave a comment